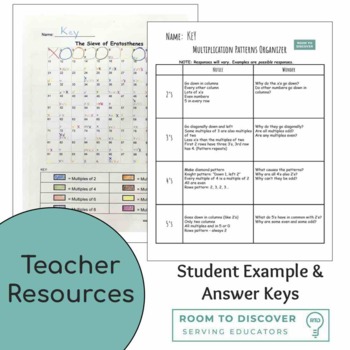
Sieve of Eratosthenes
- PDF
What educators are saying
Description
This amazing Sieve of Eratosthenes complete lesson will have your students looking at multiplication in a whole new way. It’s an “open task,” meaning that each student will learn something unique.
For some, the sieve is a way to master times tables. For others, it will help with common denominators or factoring expressions. The sieve also highlights patterns that can improve mental math with all four operations.
What's Included:
★ Introduction
★ Lesson plans
★ Two handouts with keys
★ A rubric
You might also be interested in these other resources:
★ 5 paragraph Essay Graphic Organizer
★ The Sieve of Eratosthenes Complete Lesson
★ Workshop Lesson Plan Template
★ Sieve of Eratosthenes - Worksheet Only
This product, however, will do a few things for you and your sanity to allow you to fully enjoy teaching your students:
✰ Cut down on your prep time
✰ Lesson plans are already created and ready to go
✰ Pre-organized
✰ Comprehensive and driven by proven results
✰ Free updates
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
How do I find out about and access new materials as they are posted?
Don't forget that leaving feedback earns you points toward FREE TPT purchases. I love that feedback!
✔Also, follow me and be notified when new products are uploaded.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Contact Me ☟
✰ Blog
✰ Email newsletter
✰ Facebook
✰Instagram
✰Twitter